
Using this concept, the users will get confused, especially when the market value of assets or liabilities is significantly different from the original costs. Per US GAAP, the PPE is recorded at the historical cost and required to change the value in the financial statements even if the market value of assets increases or cost principle decreases. It is incorrect to say that the historical cost accounting principle requires no change in the value of items in the Financial Statements. The Historical cost accounting principles are used mainly to record and measure the value of items in the balance sheet rather than items in the Income statements. This principle is used in both IFRS (the Principle Base) and US GAAP ( Rule Base).
Can result in distorted financial statements
Overall, the Cost Principle has its limitations and may not provide a complete and up-to-date picture of a company’s financial position. It’s essential to consider these disadvantages and evaluate the potential impact when interpreting and using financial statements based on the Cost Principle. Lastly, the Cost Principle offers transparency in financial reporting. By recording assets at their original cost, the principle provides a clear audit trail and facilitates the traceability of transactions. This transparency helps prevent manipulation or misrepresentation of financial information, contributing to the integrity of financial reporting practices. Tax laws often require that certain expenses be capitalized and amortized over some time.

Using Accounting Software to Make Using the Cost Principle Easier
A cost principle concept revolves around a significant aspect, which requires companies to record the prices of the assets that is equal to what their actual cost was at the time of purchase. This cost is not adjusted to any expense, be it the improvements done, or depreciation occurred. The cost principle might not reflect a current value of long-term property after assets = liabilities + equity so many years. For example, a building could be worth a different price now than it was 50 years ago. The historical cost principle shows the actual amount you paid for an asset, ensuring that an objective cost was recorded. The consistent use of accounting methods and procedures over time will check the distortion of profit and loss account and balance sheet and the possible manipulation of these statements.
- GAAP, or the generally accepted accounting principles, consists of 10 different principles.
- Suppose a company provides services to a client in December but does not receive payment until January of the following year.
- This isn’t just memorizing some accounting information for a test and then forgetting it two days later.
- A business asset will be worth more in good economic conditions and thus would be able to fetch a higher price as compared to selling the asset during a recession.
- For example, tax laws may require using another depreciation method or a different useful life for an asset than what is used under GAAP.
- No adjustments are made to reflect fluctuations in the market or changes resulting from inflationary fluctuations.
Small Business Resources
While historical cost accounting provides a reliable and consistent basis for financial reporting, it may not always reflect the economic reality of a company’s assets and liabilities. To address this, investors and analysts may adjust the financial statements, such as using fair value accounting, to reflect the current market value of assets and liabilities. In other words, the principle states that the value of an asset is determined by the amount paid for it at the time of acquisition, and this value remains the same until the asset is sold or disposed of. In fact, if a company were to sell its assets, the sale price might bear little relationship to the amounts recorded on its balance sheet. Thus, the cost principle yields results that may no longer be relevant, and so of all the accounting principles, it has been the one most seriously in question.
- This allows users of the financial statements, such as investors and creditors, to assess the value of the assets owned by the entity and make informed decisions.
- The historical cost principle or the cost principle provides information on the cost of an asset acquired in the past.
- The historical cost principle promotes consistency in accounting by requiring that assets and liabilities be valued at their original cost.
- For example, if a company owns a factory, it may use replacement cost accounting to measure the value of the factory based on the cost of rebuilding it using current materials and labor costs.
- An example would be the acquisition of a block of offices valued at $5,000,000.
When using other methods of accounting, like fair market value, cost verifications can be harder to provide. If you’re trying to prove the value of an item or a cost using fair market value, substantial work is involved. This can include current value for similar items, inspection on the wear and tear, and a professional appreciation. Yes, when using the cost principle, depreciation of an asset still needs to be recorded. Using the cost principle will still record the original cost of the asset. When using the cost principle, an asset’s value is easy to determine.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- These principles also make it easier to understand a business’s health and compare one or several companies’ financials over different periods.
- The store owner determines the theft dates back to around two years from various sources.
- Both benefits and drawbacks of the cost principle are explained below.
- Because of depreciation, the vehicle’s value has depreciated significantly.
During the same decade, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) worked with the SEC to develop the first formal accounting standards. In many other countries, these guidelines fall to the IFRS, established by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The roots of modern accounting principles trace back to the Stock Market Crash of 1929 and the subsequent Great Depression. Before then, companies had free rein to report their finances however they wished, often hiding losses and inflating profits through creative bookkeeping.
- The cost principle, also known as the historical cost principle, is a commonly used accounting method.
- Thus, the cost concept provides greater objectivity and greater feasibility to the financial statements.
- According to the cost principle, the purchase must be recorded on the date of its occurrence at the cash amount paid.
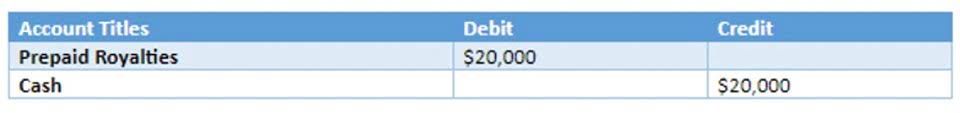
- A music company purchases the copyright to a movie from an independent filmmaker.
- Many companies trade in older work vehicles for new ones on a regular basis.
- The historical cost principle simplifies the accounting process by providing a straightforward, easy-to-apply method of valuing assets and liabilities.
As a result of this depreciation expense, the asset’s recorded value decreases throughout its useful life. The historical cost concept differs from the fair value concept, which reflects the current market value Interior Design Bookkeeping of a company’s assets. Asset valuation at the original price avoids overvaluation in a dynamic market and is a good way to figure out capital expenditures. It also makes it easy for businesses to retrieve the actual pricing of items when needed quickly.

It helps businesses assess their financial performance over time – Advantages of Historical Cost Principle

The Historical Cost Principle affects the calculation of taxable income because it determines the value of assets and liabilities used to calculate the tax base. Using the Historical Cost Principle, the tax base often equals the book value of assets and liabilities reported on the financial statements. Investors and analysts rely on financial statements to assess a company’s financial health and make informed investment decisions.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.